China’s Thorium Reactor Breakthrough and the New Era of Nuclear Energy
TechnoVita.net
A Historic Milestone in Nuclear Innovation
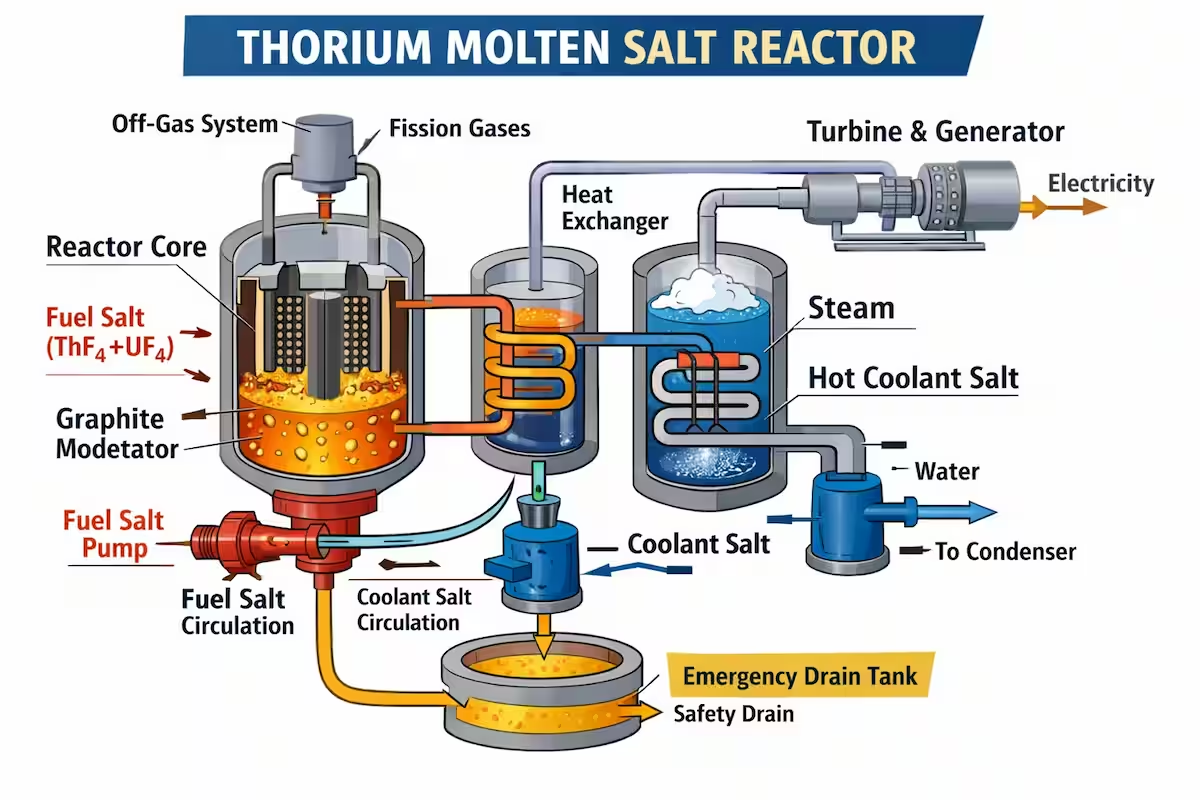
In November 2025, Chinese researchers announced a significant achievement in nuclear energy: the successful conversion of thorium into uranium fuel inside a molten salt reactor. This milestone occurred at the Thorium Molten Salt Reactor–Liquid Fuel 1 (TMSR-LF1) experimental facility in Gansu Province, operated by the Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics. The reactor transformed thorium-232 into fissile uranium-233, demonstrating for the first time that a thorium fuel cycle can work within an operational molten salt system. This makes China the first country in the world to achieve this technical feat in a functioning reactor.
Thorium has long been considered a promising alternative to conventional nuclear fuel. It is more abundant in the Earth’s crust than uranium and offers several theoretical advantages: lower long-lived radioactive waste production, improved safety features due to operation at atmospheric pressure, and reduced potential for weaponization. Molten salt reactors, which use liquid fuel mixtures instead of solid rods and water coolants, are part of a broader class known as fourth-generation nuclear systems, designed to be inherently safer and more efficient than traditional reactors.
Why Thorium Matters
The success of the TMSR-LF1 project points to a possible shift in how nuclear energy might be produced and scaled in the future. Unlike traditional uranium-based reactors, thorium reactors can operate without high-pressure coolant systems, potentially reducing the risk of catastrophic failures. In addition, thorium fuel cycles produce significantly less long-lived transuranic waste, which remains hazardous for thousands of years in conventional systems. These advantages are why thorium technology has attracted renewed interest from researchers and policymakers around the world.
China has also begun applying this technology in unconventional contexts. For example, the country has unveiled plans for thorium-powered maritime vessels, including the world’s first container ship equipped with a thorium molten salt reactor propulsion system, potentially enabling long-duration voyages with negligible emissions.
Other Recent Nuclear Energy Developments
While China’s thorium breakthrough is a headline-grabbing milestone, nuclear innovation is happening across the globe:
Advanced Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
Small modular reactors (SMRs) are emerging as a key avenue for expanding nuclear power in both industrialized and developing nations. SMRs offer smaller power outputs, reduced capital costs, and greater siting flexibility compared to traditional large reactors. Many designs use safer, passive cooling systems and can be deployed incrementally to meet growing energy demands. Governments and private companies in the United States, Europe, and Asia are actively investing in SMR technology as part of low-carbon energy strategies.
Fast Neutron and Waste-Fueled Reactors
Innovation is also occurring in reactor designs that utilize alternative cooling methods and fuel sources. For example, companies like Oklo in the U.S. are developing sodium-cooled fast reactors such as the Aurora Powerhouse, which aim to improve efficiency and waste utilization. Meanwhile, European nuclear startup Newcleo has secured investment to advance lead-cooled reactors that can use recycled nuclear waste as fuel, thereby reducing the volume and toxicity of long-term radioactive waste.
National Policy and Regulatory Support
Governments are increasingly recognizing nuclear energy as a critical component of climate mitigation and energy security. In early February 2026, the United Kingdom launched a new framework to accelerate advanced nuclear reactor development, making it easier for developers to secure planning approval, financing, and investment. The UK strategy explicitly ties nuclear development to climate goals and future industrial electricity demand, including for sectors like artificial intelligence and data centers.
Other Global Projects
Several large-scale nuclear projects are underway or planned in countries like India, where the Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (PFBR) aims to breed more fissile material than it consumes. Such reactors, if successful, could extend fuel resources and contribute to sustainable nuclear power capacity.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite these exciting developments, challenges remain. Thorium reactor technology still faces technical obstacles, including materials corrosion from high-temperature molten salt environments and the need for robust regulatory frameworks. Moreover, public perception and safety concerns around nuclear power continue to influence political support in many regions.
However, the momentum behind advanced nuclear technologies—spanning thorium systems, SMRs, and waste-utilizing reactors—suggests that nuclear power could play an increasingly important role in global decarbonization strategies. Innovations like China’s thorium fuel cycle project demonstrate that with sustained research, investment, and international collaboration, nuclear energy could become safer, cleaner, and more versatile than ever before.

You can read all comments, but you must log in to post or reply.
No comments yet. Be the first to react!